
GraphQL is a query language that allows you to get what you want from the backend, so basically, you need to describe the fields you wish to, write a query, and you are good to go. I have been working a lot with Magento GraphQL API, and I have used the Chrome extension to send requests. The number of queries I have saved has been increasing daily, and I have started looking for something that allows me to organize all my queries and mutations.
Then I remembered the Postman app, which has many beautiful features, and one tiny of them is that you can create your API collection and group all requests you want in folders.
How to export Magento GraphQL schema
The first question I asked myself was how can I export Magento GraphQL schema to the file. After some research, I found a perfect and super easy command-line tool.
The Rover CLI
The Rover CLI created by Apollo allowed me to export Magento Schema. Installation is super easy and took a few seconds (I installed it on Mac, it should be easy on Linux as well).
Use this command to install the Rover CLI:
$ curl -sSL https://rover.apollo.dev/nix/latest | shThen you need to restart a terminal or use this command to configure the rover CLI with the current shell:
$ exec /bin/zsh -lNote: this command can be different for your terminal. Please follow the instructions visible in the terminal after the Rover CLI installation.
Export Magento schema to the file
To export GraphQL Magento schema to the file, you can use this command:
$ rover graph introspect <your_magento_graphql_endpoint> > <file_name>Assuming your Magento is available on https://yoursupermagentostore.com, you want to export schema to magento.graphql file, the command you need to use looks like this:
$ rover graph introspect https://yoursupermagentostore.com > magento.graphqlImport schema to the Postman
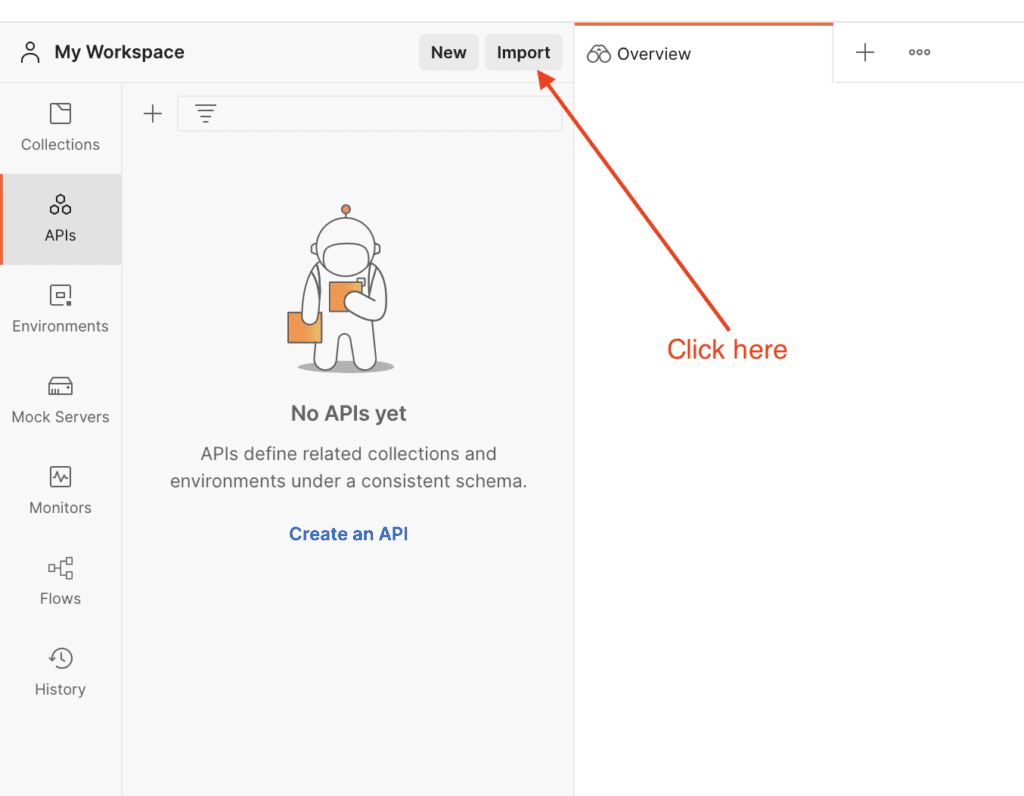
Once you export the schema to the file, you can import it into Postman. Open your Postman App, and click the import button
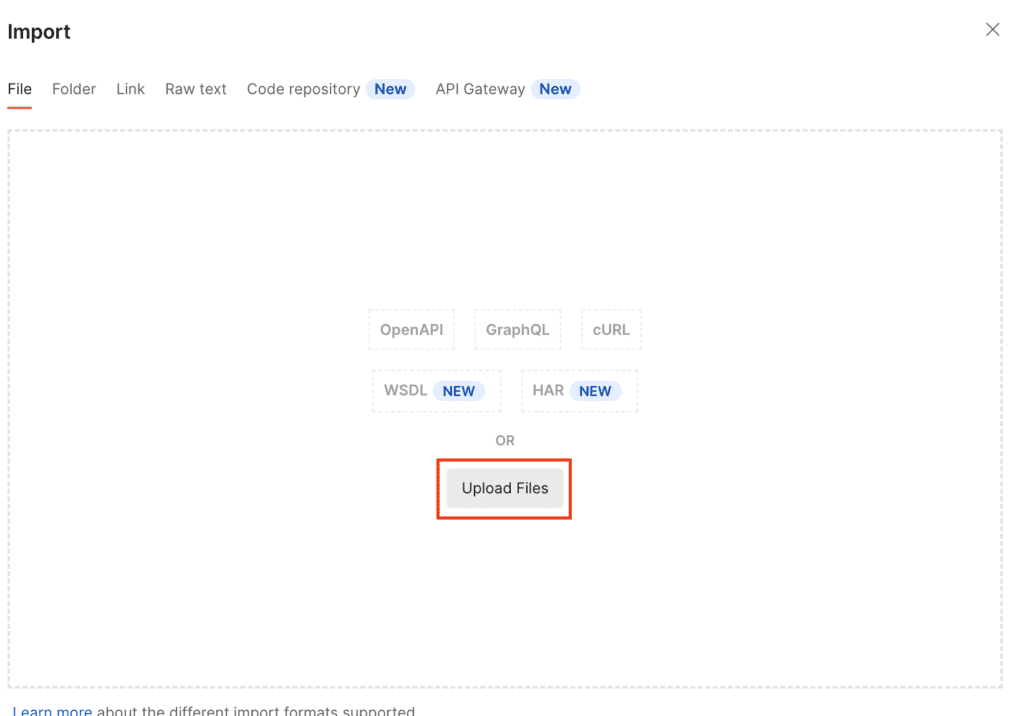
Click “Upload Files”
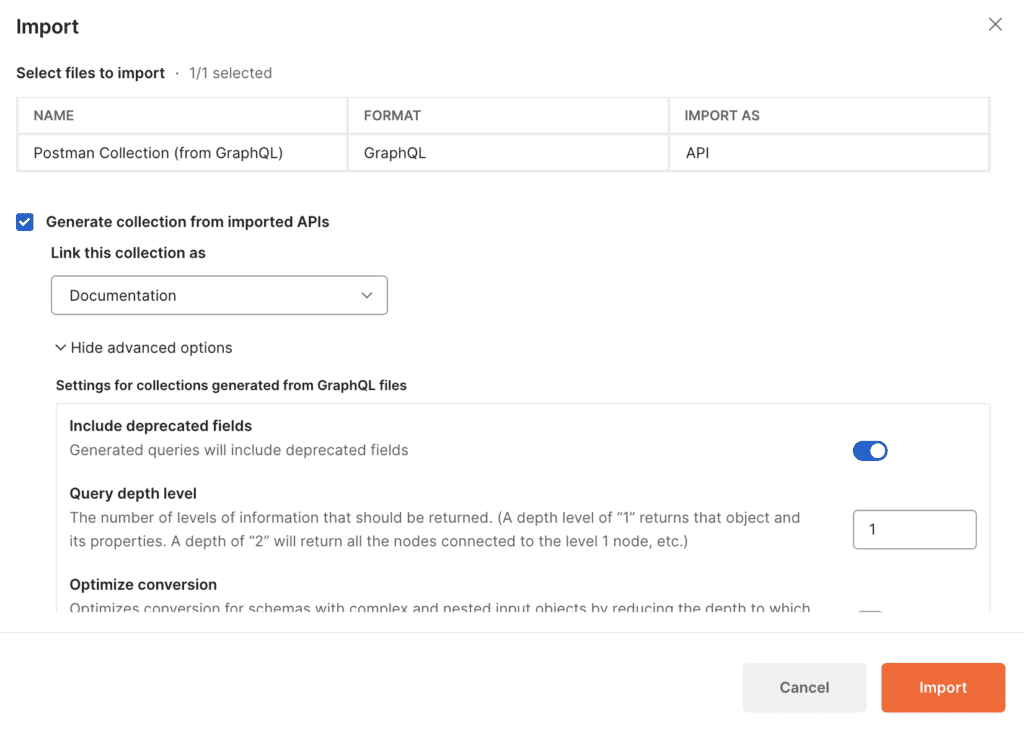
Select the file that you previously exported using the Rover CLI.
You can optionally enable the option to import deprecated fields. Next, just click Import, and your schema should be imported.
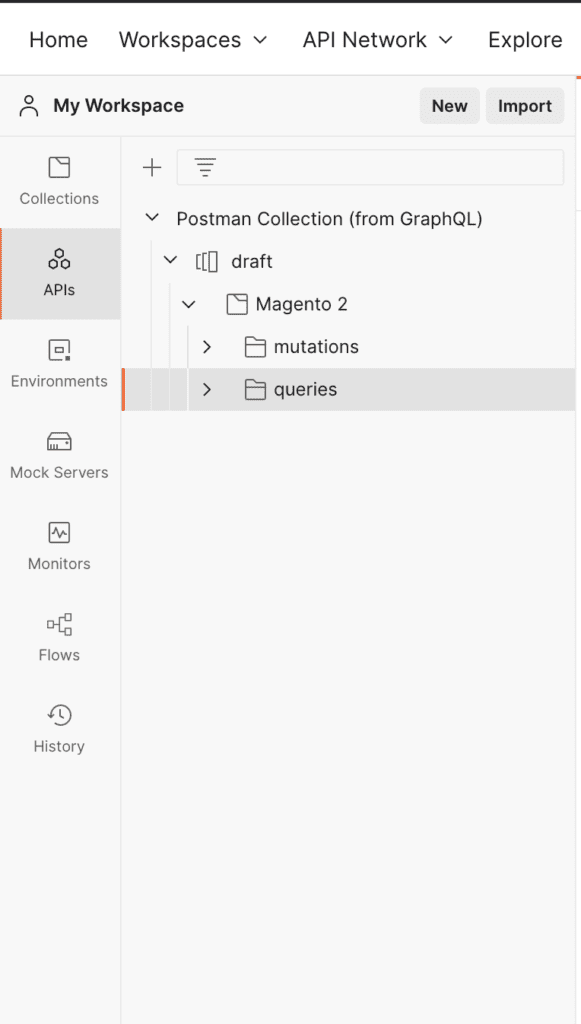
You should see queries and mutations imported:
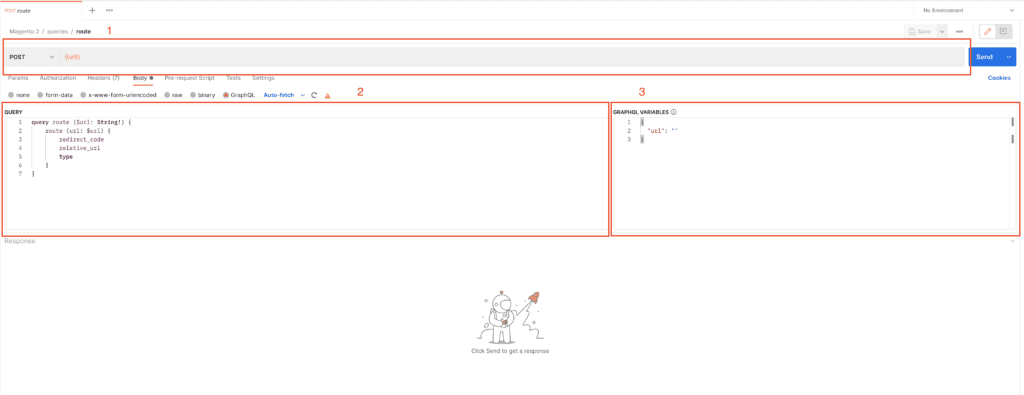
let’s take a look at one of query: route
I marked some areas in the screenshots with the red square.
-
Here you have a URL for the request. It is bound to a variable. In next step I will show you where you can add this variable
-
This is a query body
-
In this area, you can add/modify query variables
How to set variables in Postman
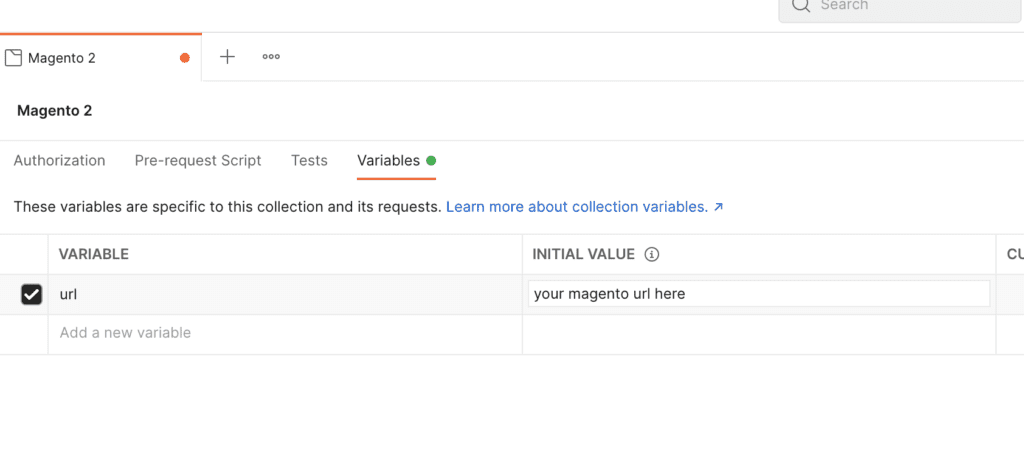
You can see variables in two ways:
-
By filling variable in Collection’s settings
-
By creating environment
This time, let’s use the first option:
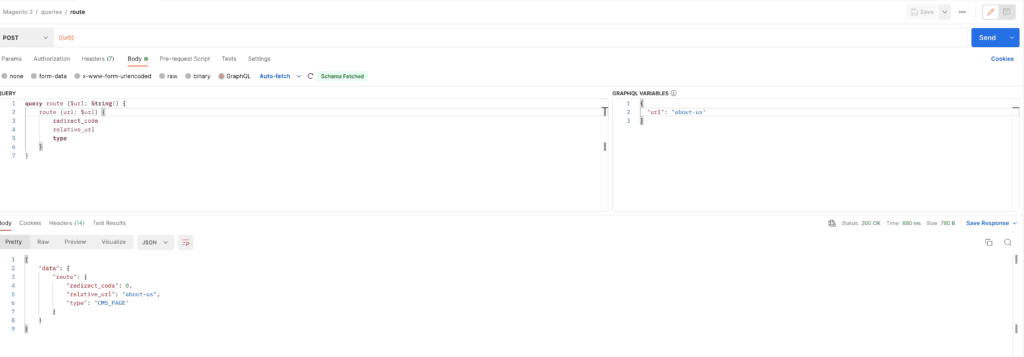
If you set up a URL to Magento correctly, a request should be sent to Magento:
Bonus: how to disable GraphQL schema introspecting in Magento
To be honest GraphQL API intersection enabled by default has danger in terms of security because it’s possible to show a GraphQL schema of any Magento shop and use it for shameful acts such as attacks on the store, data theft, etc.
Fortunately, there is an easy way to disable introspection by configuration in Magento.
To do so, please add this entry to your app/etc/env.php file:
'graphql' => [ 'disable_introspection' => true]Summary
In this short article, I showed you how to export Magento GraphQL schema and import it to Postman. On the other hand, remember that it is recommended to disable API introspection in Magento for any store on production.
