
PWA Studio is becoming increasingly popular, and I think it will be the base frontend for Magento stores in the future. This change will be a big challenge for frontend developers because working with PWA Studio is entirely different from working with the current Magento frontend.
This change will be a big challenge for frontend developers because working with PWA Studio is entirely different from working with the current Magento frontend. This change will be a big challenge for frontend developers because working with PWA Studio is entirely different from working with the current Magento frontend. The technology stack used is completely different. Therefore, different competencies and skills are required. In this article, I would like to show you the differences between the two and compare the current Magento frontend technology stack with that of PWA Studio.
Prerequisites
The most crucial difference is that the PWA Studio is a typical React app, and you don’t need special knowledge about Magento to get started with PWA Studio development.
Do you know React?
Do you know GraphQL and Apollo?
If yes, You are ready to go!
On the other hand – because it’s a React App – the typical Magento Frontend Developer will have problems getting started.
You may ask, why?
In my opinion, Magento frontend devs are not familiar(no all!) with advanced JavaScript patterns and methodologies. They work with jQuery on daily basics, sometimes with KnockoutJS.
Understanding Magento JavaScript development is quite challenging and forces you to learn specific patterns that only Magento uses.
That is the main reason why there are not too many frontend Magento developers. Almost nobody wants to learn Magento-specific stuff (who wants to use KnockoutJS in 2021, BTW?)
I had a problem returning to the “normal world” after a few years with Magento frontend development and learn React.
Ok, this was only an introduction. Take a look at the differences between Magento-monolithic frontend and PWA Studio below.
Theme vs. Application
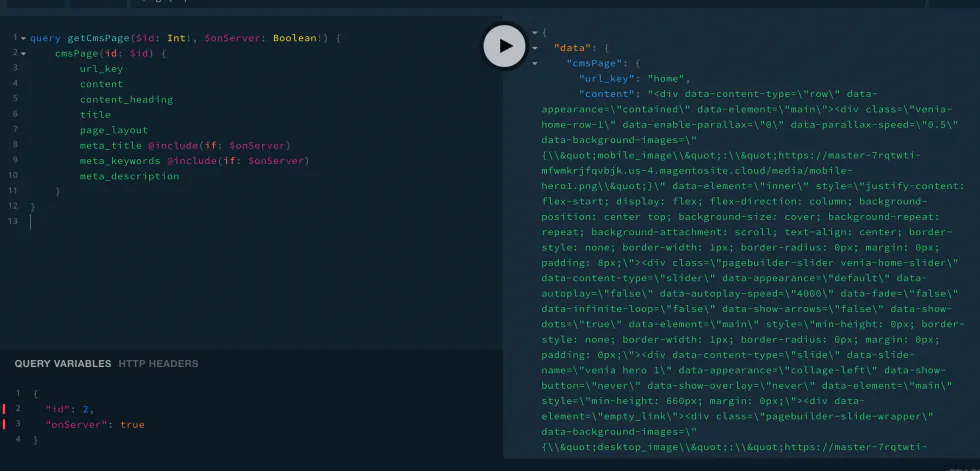
The current Magento frontend is built based on themes. There are two primary themes (Blank and Luma) that you can inherit from. The Luma theme inherits from the Blank theme, and the Blank theme overrides files from core Magento modules.
Theme code is placed in the Magento structure, and it is a part of a project. Moreover, it’s possible to create modules and manage frontend customization directly in module code.
PWA Studio uses an entirely different approach. Have you heard about headless? First of all, this means that the storefront is separated from the backend. This is the right approach because the frontend developer environment is faster and more straightforward. A Magento instance can be set up in a different place entirely. In this case, the frontend team and the backend team are independent, and developing software is more comfortable for both sides.
The only important thing when it comes to using a headless storefront with the Magento backend is data such as products, customer data, shopping cart, etc. All this data is retrieved from Magento using GraphQLqueries (it is also possible to use the REST API to get data from the backend if The GraphQL API is not available for a particular functionality).
One of the most significant advantages of using GraphQL is that a frontend developer can quickly mock sample data, and switch to real data when the backend is done.
Inheritance vs. modularity
When working with a Magento theme, frontend developers typically override templates, layouts, JS and CSS/Less files from the parent themes or modules. With multi-level inheritance and a large number of modules, a minor change can quickly become complicated.
The PWA Studio storefront is quite different and requires frontend developers to build a storefront from scratch using ready-made React components, or by making their own. PWA Studio is simply a collection of tools that are designed to facilitate your storefront development. Take a look below at the most essential parts of PWA Studio.
Peregrine
This library gives developers a set of functions responsible for providing data to visual components in their application. This is mostly achieved through hooks and talons. You may be wondering what ‘talons’ means. Talons are a specific type of hook, which are designed for particular components. For example, the useFooter talon is designed to be used with the footer component and provide it with copyright text.
import { useEffect } from "react";import { useQuery } from "@apollo/react-hooks";
/** * * @param {*} props.query the footer data query */export const useFooter = (props) => { const { query } = props; const { error, data } = useQuery(query);
useEffect(() => { if (error) { console.log("Error fetching copyright data."); } }, [error]);
return { copyrightText: data && data.storeConfig && data.storeConfig.copyright, };};Venia UI API
his is a set of visual components that you can use when building a storefront. Within this set you will find a few base components, for example, Button, ButtonGroup, Logo.
Venia Storefront (Concept)
This is a storefront built using Peregrine and Venia UI. This is a storefront demo that presents the capabilities of PWA Studio. It can be the starting point of your application, but it doesn’t have to be. Anyway it provides support for many Magento features and a few ways to extensibility.
Developer skill set comparison
I wanted to give this section the title: “Frontend Developer skill set comparison,” but sometimes, when I think about Magento Frontend Developers, I get confused, because they need to be familiar with a few non-frontend technologies like PHP and XML. I believe that for more experienced frontend developers, the right career path will be working towards becoming a Full Stack Magento Developer.
But not everyone wants to work this way, and it is not surprising that not every frontend developer will want to learn PHP. Here, PWA Studio has an advantage because it uses typical frontend tools and technologies, which are more friendly for frontend developers. Take a look at the table below where you can find a comparison of the technologies and tools used in a typical Magento frontend and in PWA Studio.
| Magento Luma | PWA Studio |
| PHP | React |
| Javascript ES5 | JavaScript ES6 |
| Rest API | GraphQl |
| jQuery | |
| Knockout | |
| Ground | Webpack |
| CSS & Less | CSS & CSS modules |
| XML | JSON |
| Magento Layouts | |
| Magento templates | |
| Magento UI Library | Venia UI |
| Magento UI Components | Peregrine |
| Composer | Yarn |
JavaScript ES5 vs. JavaScript ES6
In PWA Studio, the ES6 version of JS is standard, while Magento still uses ES5. I think that for every JavaScript developer, writing code in a newer standard is a meaningful advantage. It is true that you can also write in ES6 while working on the Magento frontend, if you take care of compilation to ES5 (I recommend using Snowdog Frontools for this). The problem is that this is a solution for new code only. You still need to remember that all of the core JavaScript code in Magento is written using the old standard, and you just have to live with it.
Grunt vs. Webpack
The Magento frontend uses Grunt as a task runner. A frontend developer can compile Less files and run unit tests using Grunt, but in fact, using Grunt is not necessary. For example, a developer can compile styles using a client-side compilation workflow. PWA Studio uses Webpack, and this tool is very different to Grunt. Webpack is a module bundler, and it is responsible for compiling the whole PWA Studio application.
Less vs. CSS modules
CSS modules are an interesting approach. The key feature is that all styles are used locally, i.e., within one component. This is an entirely different approach from the current Magento frontend, where styles are global.
Knockout, jQuery, Magento UI components vs. React
In my opinion, the Magento frontend’s biggest problem is that there is a mix of technologies and this results in chaos. Famous UI Components – a result of the Magento Core Team’s imagination – are a combination of JavaScript, PHP, and XML, and digging deeper, it turns out that Knockout is mixed with jQuery. It turns out that Knockout is mixed with jQuery.
In PWA Studio, React is used, and the best thing is that a Frontend developer doesn’t need to know PHP, XML, or any other non-frontend tools and technologies.
Magento templates vs. JSX
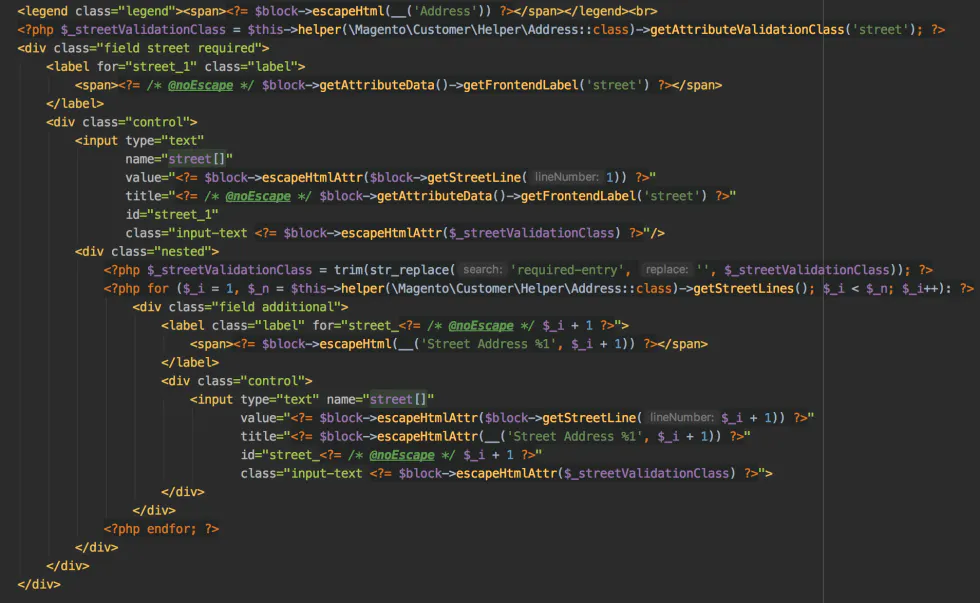
Also, there is another type of template that is used by Magento UI Components. These templates are written as HTML files, and within them, you can find static HTML code mixed with KnockoutJS bindings.
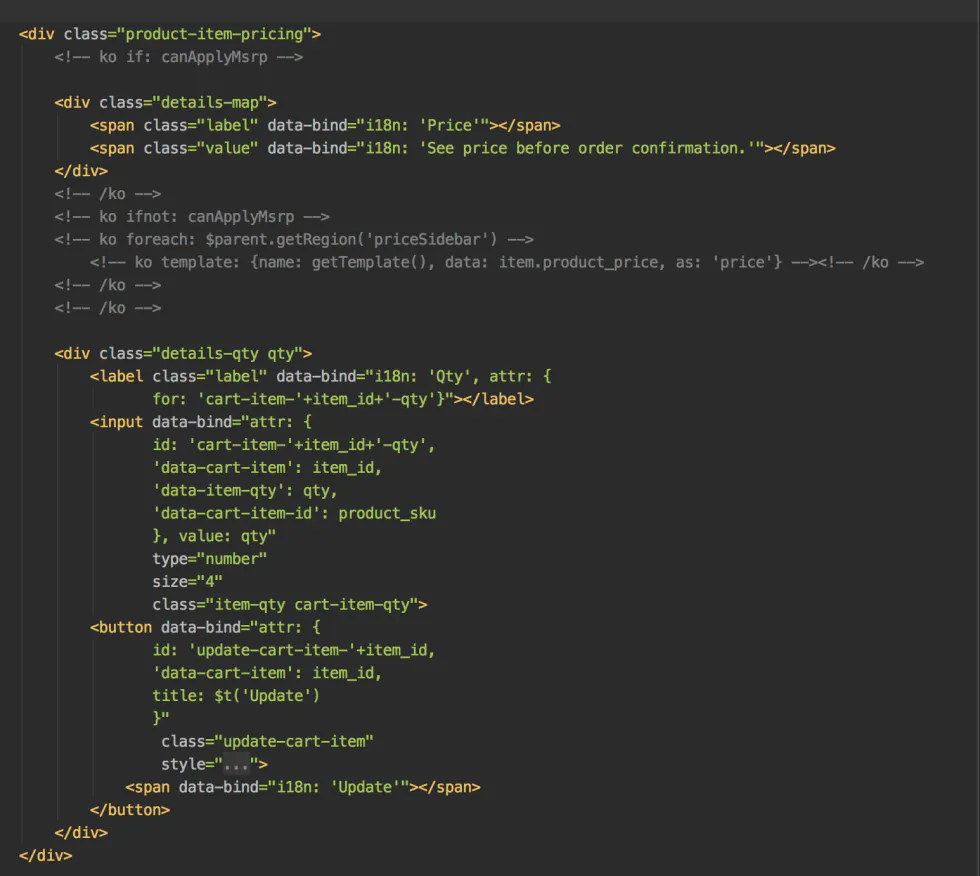
Now, just as a comparison, take a look at an example piece of code for a PWA Studio view component:
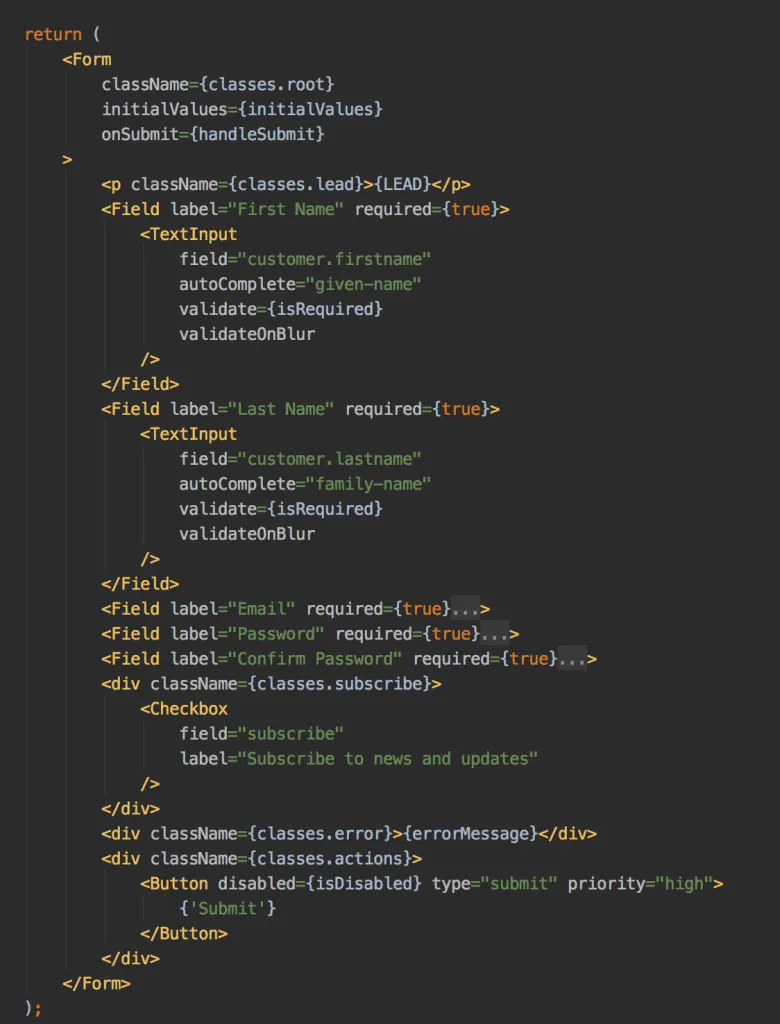
Summary
PWA Studio is different from the current Magento frontend in every area. The most significant advantage (for developers) is that PWA Studio is more developer-friendly. This is the future for Magento Frontend developers, and I am keeping my fingers crossed for this project. Also, keep in mind that there are alternatives to PWA Studio, for example: Vue Storefront. So maybe PWA technology is the future of e-commerce? What do you think? Feel free to post comments.

 Github
Github Linkedin
Linkedin